Hello Dev.
Applications require some tasks to be run periodically on the server. it is able to be sending promotional emails, optimizing database, creating backups or generating site visitors report. To automate these tasks, a task scheduling system is required. Laravel Cron JOB gives an elegant undertaking Scheduling mechanism.
Cron
Cron is a time-based task scheduler in Unix/Linux operating system. It runs shell commands at a pre-specified time period. Cron makes use of a configuration file referred to as crontab also known as Cron table to manage the undertaking scheduling procedure.
Crontab includes all the Cron jobs associated with a particular task. Cron jobs are composed of two elements, the Cron expression, and a shell command that needs to be run.
Laravel Cron Job
Laravel Cron Job is an built in task manager that offers your applications the potential to execute specific commands like sending a slack notification or getting rid of inactive user at a periodic time. we are using the version of Laravel 5.6.
You need a Linux Operating System to run Cron Jobs. This tutorial also assumes a fair knowledge of PHP and Laravel.
Creating a new Project
In this tutorial, we will create a simple laravel application to demonstrate task scheduling. Create a new Laravel project by running the following command.
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel cron
Create your Scheduled Task in Laravel
There are different ways you can define scheduled tasks in laravel. Let’s go through each of them to understand how they can be implemented in Laravel.
Create New Artisan Command
cd into your project and run the following command to create a new artisan command class:
php artisan make:command WordOfTheDay
The above command will create a new command file, WordOfTheDay.php, in the app/Console/Commands directory. Navigate to the file and you will find the following code in it:
WordOfTheDay.php
<?php
namespace App\Console\Commands;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
class WordOfTheDay extends Command
{
/**
* The name and signature of the console command.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $signature = 'command:name';
/**
* The console command description.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $description = 'Command description';
/**
* Create a new command instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
}
/**
* Execute the console command.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function handle()
{
//
}
}
In this code, the following line contains the name and the signature of the command.
protected $signature = 'command:name';
Replace the words command:name with word:day. This is what we will call this when running the command to perform the task.
protected $signature = 'word:day';
Above code also contains the description property. This is where you place the actual description of what this command will do. Description will be shown when the Artisan list command is executed alongside the signature. Change the description of the command to:
protected $description = 'Send a Daily email to all users with a word and its meaning';
Handle method is called whenever the command is executed. This is where we place the code for doing the specific task. This is how the WordOfTheDay.php file looks with the handle method and all other changes in place:
WordOfTheDay.php
<?php
namespace App\Console\Commands;
use App\User;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Mail;
class WordOfTheDay extends Command
{
/**
* The name and signature of the console command.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $signature = 'word:day';
/**
* The console command description.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $description = 'Send a Daily email to all users with a word and its meaning';
/**
* Create a new command instance.
*
* @return void
*/
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
}
/**
* Execute the console command.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function handle()
{
$words = [
'aberration' => 'a state or condition markedly different from the norm',
'convivial' => 'occupied with or fond of the pleasures of good company',
'diaphanous' => 'so thin as to transmit light',
'elegy' => 'a mournful poem; a lament for the dead',
'ostensible' => 'appearing as such but not necessarily so'
];
// Finding a random word
$key = array_rand($words);
$value = $words[$key];
$users = User::all();
foreach ($users as $user) {
Mail::raw("{$key} -> {$value}", function ($mail) use ($user) {
$mail->from('[email protected]');
$mail->to($user->email)
->subject('Word of the Day');
});
}
$this->info('Word of the Day sent to All Users');
}
}
Above code will select a random word from the array and send emails to every user with the word.
Registering the Command
Now that you have created the command, you will need to register it in the Kernel.
Go to app/Console/Kernel.php file that looks like this
Kernel.php
<?php
namespace App\Console;
use Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Console\Kernel as ConsoleKernel;
class Kernel extends ConsoleKernel
{
/**
* The Artisan commands provided by your application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $commands = [
//
];
/**
* Define the application's command schedule.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule $schedule
* @return void
*/
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
// $schedule->command('inspire')
// ->hourly();
}
/**
* Register the commands for the application.
*
* @return void
*/
protected function commands()
{
$this->load(__DIR__.'/Commands');
require base_path('routes/console.php');
}
}
In this file, we register the command class in the commands property and we schedule commands to be executed at periodic intervals in the schedule method. This is where we handle all the Cron Jobs in Laravel.
Change this file with the contents below. We have simply added our WordOfTheDay class to the commands property and schedule it to run every day.
<?php
namespace App\Console;
use Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Console\Kernel as ConsoleKernel;
class Kernel extends ConsoleKernel
{
/**
* The Artisan commands provided by your application.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $commands = [
Commands\WordOfTheDay::class,
];
/**
* Define the application's command schedule.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule $schedule
* @return void
*/
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->command('word:day')
->daily();
}
/**
* Register the commands for the application.
*
* @return void
*/
protected function commands()
{
$this->load(__DIR__.'/Commands');
require base_path('routes/console.php');
}
}
Now, if you run the php artisan list command in the terminal, you will see your command has been registered. You will be able to see the command name with the signature and description.
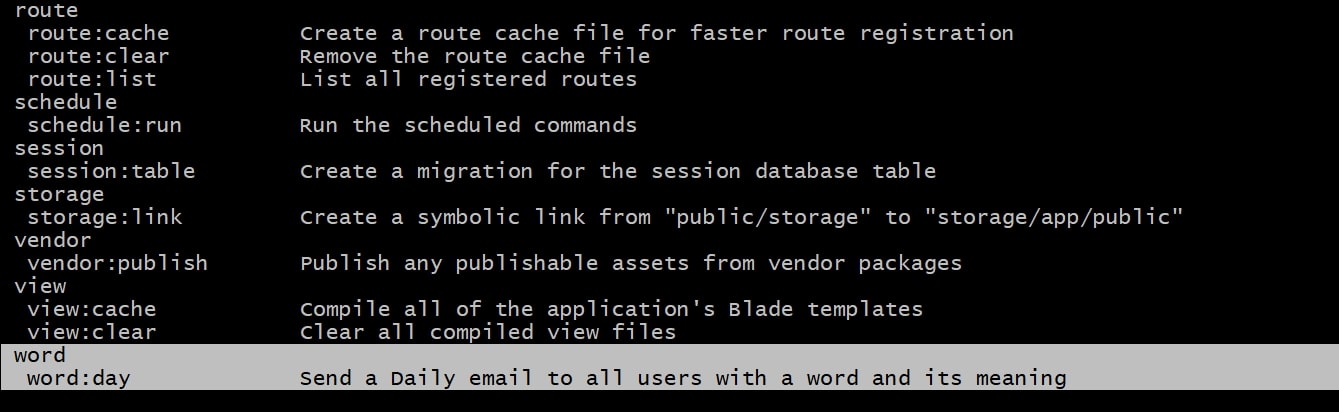 Setup, database and mail credentials in the .env file and make sure you have users in the database. Execute the command itself on the terminal:
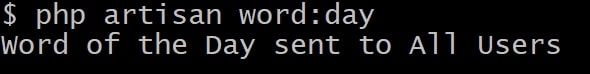
Setup, database and mail credentials in the .env file and make sure you have users in the database. Execute the command itself on the terminal:
php artisan word:day
Command will be executed with the signature that is placed in protected $signature = 'command:name'. You will also see the log message in the terminal.
Using Closure/Callback Method
Laravel Task Scheduler allows you to execute a callback or a closure periodically using the call method. Let’s add code in the schedule method of app/Console/Kernel.php Here’s the contents of the class with only the schedule method.
<?php
namespace App\Console;
use App\User;
use Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Console\Kernel as ConsoleKernel;
class Kernel extends ConsoleKernel
{
/**
* Define the application's command schedule.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule $schedule
* @return void
*/
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->call(function () {
User::where('spam_count', '>', 100)
->get()
->each
->delete();
})->hourly();
}
}
We have passed the closure as the first parameter to the call method. We have set the frequency of the task to hourly, so it will execute every hour. In the call method, we are simply removing users with spam count of more than 100.
Exec Command
Laravel also allows you to schedule shell commands so that you could issue commands to the operating system and external applications. We use the exec method to execute a shell command.
Here’s a simple example, that allows you to take backup of your code every month.
<?php
namespace App\Console;
use Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Console\Kernel as ConsoleKernel;
class Kernel extends ConsoleKernel
{
/**
* Define the application's command schedule.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule $schedule
* @return void
*/
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->exec(
'cp -r ' . base_path() . " " . base_path('../backups/' . date('jY'))
)->monthly();
}
}
exec method will run the command you would pass as the first argument. In the code above, it simply copies your laravel project to the backups folder. The backups folder will be followed by the day of the month and a numeric representation of the year. You can also schedule Laravel Jobs in the Task Scheduler the same way we scheduled Artisan commands and closures. Let’s take a look at the Task Scheduler in detail.
Task Scheduler in Laravel
Task Scheduler in Laravel executes the artisan command, shell, or a callback periodically on the defined time. To do this, we use the schedule method in app/Console/Kernel.php like we discussed earlier.
protected function schedule(Schedule $schedule)
{
$schedule->command('word:day')
->daily();
}
$schedule->command('word:day') is where we define which command needs to be executed and ->daily(); defines the frequency of execution. A list of additional schedule constraints may be find HERE
Starting the Laravel Scheduler
Let’s setup the Cron Jobs to run automatically without initiating manually by running the command. To start the Laravel Scheduler itself, we only need to add one Cron job which executes every minute. Go to your terminal, ssh into your server, cd into your project and run this command.
crontab -e
This will open the server Crontab file, paste the code below into the file, save and then exit.
* * * * * cd /path-to-your-project && php artisan schedule:run >> /dev/null 2>&1
Do not forget to replace /path/to/artisan with the full path to the Artisan command of your Laravel Application.
One of the most important advantages of Laravel Task Scheduler is that we can focus on creating commands, writing logic and Laravel will take care of the rest. It is manageable by other co-workers because it is now tracked by version control.
i'm hoping it assist you to, thanks for visit my article if you like my article then proportion together with your friend and social platform.


